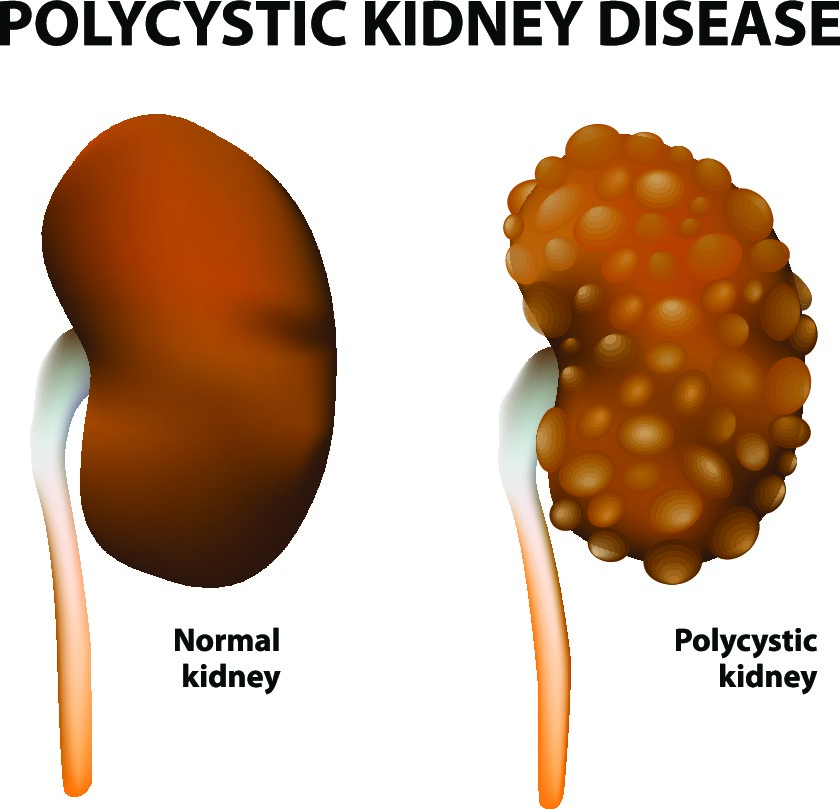
According to the National Institute of Health, autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) affects 1 in every 400 to 1,000 people globally. Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is one of the most common genetic disorders, impacting approximately 500,000 people in the United States. Polycystic Kidney Disease Drug Pipeline Analysis Characterized by the development of fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys, ADPKD can lead to kidney failure, making it a major cause of end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Despite its prevalence, there remains a significant unmet need for more effective therapies to manage the condition and improve patients’ quality of life. Consequently, there has been an increased focus from pharmaceutical companies and research institutions on developing innovative treatments, leading to a growing number of drugs in the pipeline.
Get a Free Sample Report with a Table of Contents: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/clinical-trials/polycystic-kidney-disease-drug-pipeline-analysis/requestsample
Overview of the Polycystic Kidney Disease Drug Pipeline
The global drug pipeline for polycystic kidney disease (PKD) has seen considerable advancement in recent years, with a growing number of pharmaceutical companies and research institutes investing in innovative treatments. The primary goal is to slow the progression of kidney cyst growth and delay the onset of kidney failure, which is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in ADPKD patients.
As of 2023, several promising therapies are in various stages of clinical development, including small molecule inhibitors, gene therapies, and biologics. The focus is on addressing the root causes of cyst formation and kidney damage, with the aim of offering patients treatments that go beyond symptom management.
Polycystic Kidney Disease Drug Pipeline Dynamics
The dynamics of the ADPKD drug pipeline are shaped by several factors:
- Unmet Medical Need: The current treatment options for ADPKD are limited, and there is no cure. The only FDA-approved drug for ADPKD, Tolvaptan, is effective at slowing the progression of cyst growth, but it has limitations, including the need for careful monitoring of liver function. The need for more effective, less toxic, and easier-to-use treatments is a major driver of pipeline development.
- Targeted Approaches: As research into the genetic and molecular mechanisms of ADPKD progresses, targeted therapies that can address specific pathways involved in cyst formation are gaining traction. These therapies aim to slow the growth of cysts, reduce fibrosis, and preserve kidney function.
- Gene Therapy: Gene-editing technologies such as CRISPR are providing exciting new possibilities for the treatment of genetic diseases, including ADPKD. Researchers are exploring ways to correct the genetic mutations that cause the disease, offering potential long-term solutions.
- Collaboration and Partnerships: Leading pharmaceutical companies and biotech firms are increasingly forming partnerships to accelerate the development of ADPKD therapies. These collaborations are helping to pool resources, share expertise, and expedite clinical trials.
- Clinical Trials and Regulatory Pathways: The regulatory approval process for ADPKD drugs is complex and varies by region. However, with increased collaboration between industry stakeholders and regulatory bodies like the FDA and EMA, clinical trials are becoming more streamlined, and the pathway to market for promising treatments is becoming clearer.
Read Full Report with Table of Contents: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/clinical-trials/polycystic-kidney-disease-drug-pipeline-analysis
External Trends Influencing the Polycystic Kidney Disease Drug Pipeline
Several external trends are influencing the ADPKD drug pipeline, including:
- Increased Awareness and Advocacy: Advocacy groups such as the PKD Foundation are playing a pivotal role in raising awareness of ADPKD, educating both the public and healthcare providers about the disease, and promoting research into new treatments.
- Advancements in Precision Medicine: With the increasing understanding of the genetic and molecular factors that contribute to ADPKD, there is a shift toward precision medicine. This approach allows for more targeted therapies that are tailored to individual patients based on their genetic profile, leading to better outcomes and fewer side effects.
- Government Initiatives and Funding: Governments around the world are increasing their funding for research into rare diseases, including ADPKD. This financial support is helping to drive innovation and ensure that critical research into effective therapies continues.
- Focus on Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): As chronic kidney disease (CKD) continues to rise globally, there is growing interest in therapies that can prevent or delay the progression of kidney diseases like ADPKD. This trend is pushing pharmaceutical companies to prioritize research into kidney diseases, with ADPKD being one of the most significant areas of focus.
Polycystic Kidney Disease Drug Pipeline Segmentation
The ADPKD drug pipeline can be segmented based on several factors, including the type of therapy, stage of development, and targeted mechanism of action. Here are some key segments:
- Therapy Type:
- Small Molecule Drugs: These drugs aim to target specific pathways involved in cyst formation and kidney damage. Tolvaptan, the most commonly used drug for ADPKD, belongs to this category. Other small molecule drugs in the pipeline target the cAMP/PKA pathway, which is known to be involved in cyst growth.
- Gene Therapy: Gene-editing techniques like CRISPR are being explored to correct the genetic mutations that cause ADPKD, offering a potential cure for the disease.
- Biologics: Biologic treatments such as monoclonal antibodies are being investigated to modulate specific immune or molecular pathways that contribute to cyst formation and kidney fibrosis.
- Cell Therapy: Stem cell-based therapies are another area of interest for ADPKD treatment, aiming to regenerate damaged kidney tissue and restore kidney function.
- Small Molecule Drugs: These drugs aim to target specific pathways involved in cyst formation and kidney damage. Tolvaptan, the most commonly used drug for ADPKD, belongs to this category. Other small molecule drugs in the pipeline target the cAMP/PKA pathway, which is known to be involved in cyst growth.
- Stage of Development:
- Preclinical: Several potential therapies are still in the preclinical stage, where they are being tested in animal models to assess safety and efficacy.
- Phase 1: Early-stage human trials are underway for some small molecules and biologics aimed at slowing cyst growth and improving kidney function.
- Phase 2: Phase 2 trials are focused on evaluating the efficacy and safety of drugs in a larger group of patients, and several candidates are showing promise.
- Phase 3: Drugs in Phase 3 trials are close to reaching the market and are undergoing large-scale testing to confirm their safety and efficacy.
- Preclinical: Several potential therapies are still in the preclinical stage, where they are being tested in animal models to assess safety and efficacy.
Recent Developments in the Polycystic Kidney Disease Drug Pipeline
Some recent breakthroughs in the ADPKD drug pipeline include:
- Novartis Pharmaceuticals: Novartis is developing Lasmiditan, a drug aimed at targeting specific molecules involved in cyst formation. Early studies have shown that Lasmiditan can significantly reduce cyst growth and improve kidney function.
- Palladio Biosciences: Palladio’s lead drug candidate, PB-105, is a novel therapy designed to block the cAMP pathway, which is known to play a crucial role in cyst development. Early-phase trials have shown encouraging results in reducing cyst size and improving kidney function.
- Regulus Therapeutics Inc.: Regulus is focusing on RG-101, an RNA-based therapy aimed at targeting the gene expression pathways that lead to cyst formation in ADPKD. Early-stage trials suggest that RG-101 may offer a new treatment option for ADPKD patients with genetic mutations.
Polycystic Kidney Disease Drug Pipeline Growth and Market Outlook
The ADPKD drug pipeline is expected to grow significantly over the next decade. This growth will be driven by advancements in precision medicine, the increasing understanding of the genetic basis of ADPKD, and the rise of innovative therapies such as gene therapy and biologics.
The market for ADPKD therapies is poised to expand as more drugs are developed and approved. The global market for kidney disease treatments is expected to reach USD 26.4 billion by 2025, and ADPKD drugs will constitute a substantial portion of this market.
COVID-19 Impact on the Polycystic Kidney Disease Drug Pipeline
The COVID-19 pandemic had a temporary impact on clinical trials for ADPKD, with many trials being delayed or paused due to social distancing measures and disruptions in healthcare services. However, the pandemic also accelerated the adoption of digital health technologies, such as virtual trials and remote monitoring, which helped mitigate some of the impacts on drug development.
Researchers and pharmaceutical companies have adapted to the challenges posed by COVID-19, and clinical trials are now resuming, with modifications to ensure patient safety and compliance with health protocols.
Key Players in the Polycystic Kidney Disease Drug Pipeline
- Palladio Biosciences
- Regulus Therapeutics Inc.
- Novartis Pharmaceuticals
These companies are leading the charge in developing innovative therapies for ADPKD and are expected to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of ADPKD treatment.
(FAQ)
1. What is Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD)?
PKD is a genetic disorder characterized by the growth of numerous cysts in the kidneys, which can lead to kidney failure. There are two main forms of PKD: autosomal dominant PKD (ADPKD) and autosomal recessive PKD (ARPKD).
2. How is ADPKD diagnosed?
ADPKD is typically diagnosed through imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI, which can detect cysts in the kidneys.
3. What are the treatment options for ADPKD?
Currently, treatment options focus on managing symptoms and slowing the progression of the disease. Tolvaptan is the only FDA-approved drug for ADPKD. Other treatments are being investigated, including gene therapies and biologics.
4. What is the outlook for the ADPKD drug pipeline?
The ADPKD drug pipeline is expected to see significant growth in the coming years, with a number of promising therapies in development that could offer better outcomes for patients.